Defining VAT Rules for Events
To comply with Place of Supply requirements, you can use the VAT Rules table to define when not to charge VAT tax on taxable functions. These rules have limited scope: they only apply to taxable functions of VAT-enabled events that have a VAT Rule specified in the event’s definition. These special rules are optional, and you do not need these rules at all unless your organization faces one of these situations:
- You hold online (virtual) events. The new Place of Supply rules have requirements that apply to online events, as these specifically fall into the new “General Rules” (under Article 44 and 45).
- You hold in-person events in another EU country. If you hold an event in another EU country that has different guidelines for when to charge VAT, then you need to define a new rule set.
- Your tax advisor determines that the default approach of charging VAT to all non-exempt registrants is insufficient.
Warning!
Consult your tax advisor or audit firm for questions and validation of your rule sets.
You can create as many rule sets as you need to handle the situations you must support, if any. In all cases, your registrants — whether registered in Desktop, Web, or Public views — see only confirmation that their fees include the required VAT taxes.
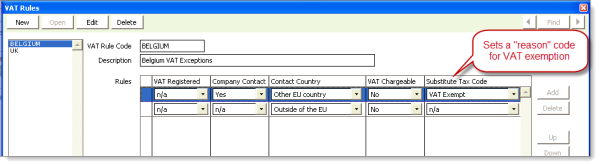
- VAT Registered – whether the registrant has a VAT Registration number entered.
- Company Contact — a registrant whose own record or whose parent record has a member type that is defined as a Company Record in the Member_Types table.
- Contact Country — refers to the country specified in the registrant's address (regardless of parent record) as determined using the VAT country codes you defined.
- Same as place of supplier — the registrant is in the same VAT country as the event’s entity.
- Other EU Country – the registrant is in a different EU country from the event’s entity.
- Outside of the EU – the registrant is outside of the EU.
- VAT Chargeable — The Yes option exists for rare cases in which you need to insert a Yes rule to ensure a correct VAT charging situation isn't overridden by a more general No rule below it.
- Substitute Tax Code — This optional field is available only when VAT Chargeable is No. It lets you select one of your zero-rated VAT tax codes as the "reason" for why the situation is not taxable. Examples: the contact is VAT Exempt, is registered in a different EU country, or is outside of the EU altogether. These codes allow you to report and document tax exemptions as required.
Note: Include both Name_Fin.VAT_REG_NUMBER and Name_Fin.USE_VAT_TAXATION in the User Defined Company Flow Down list, in Customers > Set up module, Advanced.
Where do VAT rules apply? If an event function is marked Taxable, VAT taxes can be charged. If the event itself also specifies use of a VAT Rule, iMIS determines whether to charge VAT according to your rules of exclusion.
How do rule sets work? When a VAT event specifies a rule set, iMIS determines whether to charge the registrant VAT by testing each rule for a match. Starting with the top rule, iMIS stops only when all three conditions (whether VAT Registered, whether a Company Contact, and location) are met. If no rules are satisfied, VAT is charged as usual.
Example rule set: Online Events
| VAT Registered | Company Contact | Contact Country | VAT Chargeable |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
n/a |
Other EU country |
No |
Example rule set: Belgium events in France
| VAT Registered | Company Contact | Contact Country | VAT Chargeable |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
n/a |
Same as place of supplier |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
Same as place of supplier |
No |
To set up entities for other EU countries
If you hold events within the EU but outside of your EU country, you may need to set up multiple entity processing for each country involved in order to keep your financial records separate. The issue is [1] whether you hold an event in another EU country (say, a Paris conference for your Brussels-based association) and [2] whether that country has different guidelines for when to charge VAT.
- Define the entities (see Defining an organizational entity) for which you need to keep separate financial records.
- Select File > System Setup, Organization Names.
- Select New and create organizations for each additional EU country, ensuring the Taxation Method is VAT and completing the VAT fields that appear.
- Enable multi-entity processing (see Enabling multi-entity processing).
- From AR/Cash > Set up module, select Edit and enable Multiple Entities.
- If needed, change the default entity for Events.
- Define default accounts (see Defining default general ledger accounts) for your entities.
- Set up cash accounts (see Setting up cash accounts) for your entities.
- Set up Due To/Due From processing (see DueTo/DueFrom processing).
- Verify the Default country for the website (RiSE > Set up web components > General configuration).
- When defining events that need this special VAT tracking, select your new entity codes as needed.
To define a set of VAT Rules
- Open Events > Set up module, VAT Rules and select New.
- Create a VAT Rule Code; add a Description (optional) to explain the rule set and to display in the drop-down list during Event definition.
- Change the n/a (not applicable) defaults to Yes and No as needed to define the test for evaluating the taxability. The n/a values behave as “either Yes or No” in the evaluation.
- Select Add to activate rows for any additional rules you need; note that Delete removes only the row that is currently highlighted.
- Use Up and Down to arrange the rules in the order you want them to evaluate, from the top.
- Select Save, then close the window or select New to create another rule set.
To apply VAT Rules
Each event can use one set of rules that you defined for its taxable functions, but the registration process still lets you override function-level tax codes.
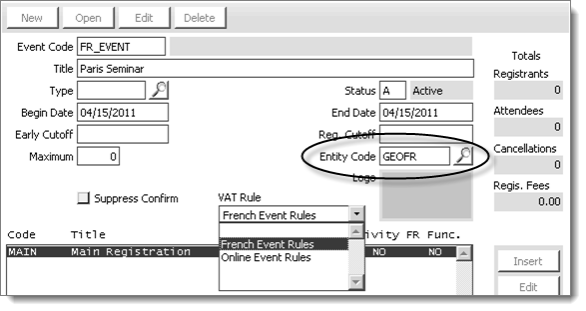
- Select Events > Define an event, select New or Edit, and select the correct VAT Entity Code for the accounting of these transactions.
- Apply a VAT rule set to your VAT event: select a VAT Rule from the drop-down list.
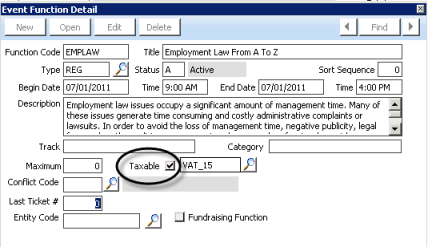
- When defining each event function, enable the Taxable option as appropriate.
- During registration, be aware that in some cases (such as when a registrant's company is VAT Exempt), enabling Add to master during registration causes taxes to be recalculated on functions, changing their cost.
If this happens, you are prompted to click OK, confirm the registration details, adjust the payment amount as needed, then click Save.
More:
How VAT Rules test Contact Country
Examples of VAT Rules