Last updated on: February 13, 2026
A media asset is any place where an ad can run, such as:
- Print magazine
- Website
- Newsletters
- Television
- Sponsorship
- Booth
Each media asset has a distinct name and code. The media kit is a public statement of advertising options, when they are available, what they cost, and other details. Media assets are the space in which an advertisement can exist. Create new media assets when you have new advertisement space to sell.
Example: The Annual Conference event is quickly approaching, and sponsors have started inquiring about securing advertisement space on your Annual Conference website homepage and at the actual event. The first step is to create a media asset for your Annual Conference website.
In This Article
Creating the product
All media orders are associated with at least one media asset. When media orders are created, the item code selected in the media asset is the charged product listed on the invoice.
Do the following to create a new Item code for an advertising media asset:
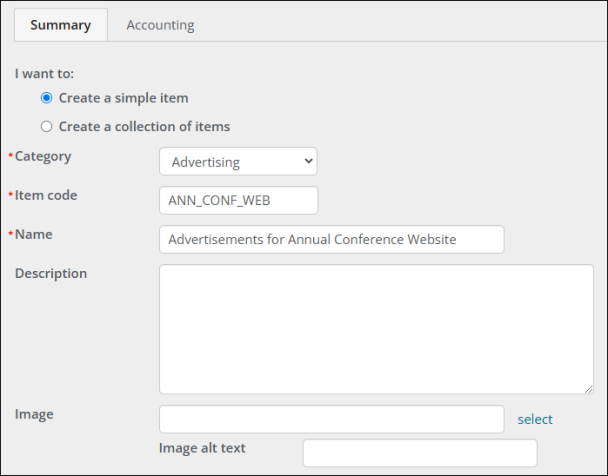
- Go to Commerce > Add product.
- From the Category drop-down, select Advertising.
- Enter an Item code and Name that are descriptive of the media asset.
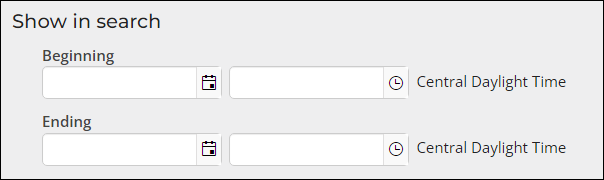
- To ensure the advertising product does not appear in search results, set the Ending date to a past date.
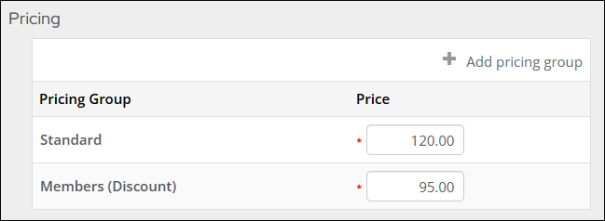
- Enter a Standard price and Members (Discount). These prices do not appear anywhere on the media order.
- Click the Accounting tab and define an Income account, if different than the Default.
- Click Save & Exit.
Important! It is important to review the selected product category (Settings > Commerce > Product categories) to confirm the category is not configured for inventory, shipping, or handling charges. The selected product category can be commissionable, part of a product kit, or taxable.
Creating the media asset
Do the following to create a new media asset:
- Go to Advertising > Settings > Media assets.
- Click Create Media Asset:
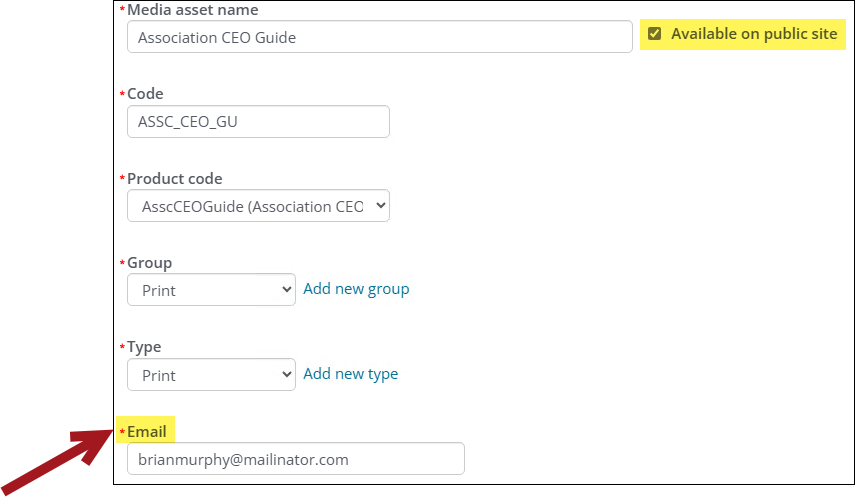
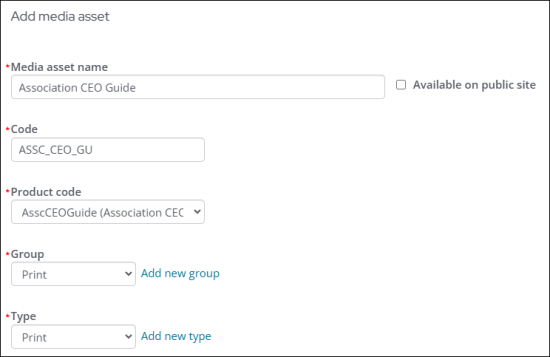
- Media asset - Enter the name of the media asset. The name must be unique.
- Available on public site - Enable Available on public site if the media asset will be available for users to purchase on the public site. If enabled, an email is required.
- Code - Enter the code of the media asset. The code must be alphanumeric and unique.
- Product - From the drop-down, choose the item code. When media orders are created, the product item code is the charged product listed on the invoice. The Product drop-down contains all commerce products with a category of Sales.
- Group - From the drop-down, choose a group. Media assets are grouped in various categories for better overview of data, for example, Print Publications, Digital Entities, or Events. To create a new group, click the add (+) icon, and enter the Name of the group.
- Type - From the drop-down, choose the type, for example, Print, Digital, or Event. To create a new type, click the add (+) icon, and enter the Type name.
- Enter an Email, Phone, and Address that will be added to the insertion order.
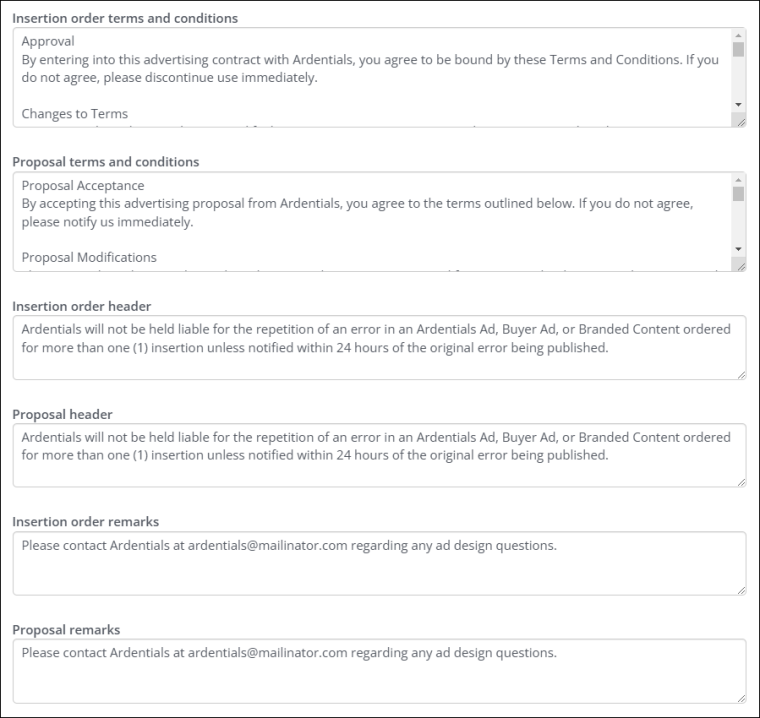
- Insertion order terms and conditions – Enter the terms and conditions for the insertion order.
- Proposal terms and conditions - Enter the terms and conditions for the proposal.
- Insertion order header – Enter a header for the insertion order.
- Proposal header – Enter a header for the proposal.
- Insertion order remarks – Enter any remarks that need to be added to the insertion order.
- Proposal remarks – Enter any remarks that need to be added to the proposal.
- Upload Logo - Click Upload Logo and select a logo for this media asset. Acceptable file types are .png or .jpg.

- Click Create Media Asset.
- To edit the media asset, click the pencil icon. The same window opens where you can edit details of the media asset.
Deleting a media asset
To delete a media asset, do the following:
Note: You cannot delete media assets used by existing media orders.
- Go to Advertising > Settings > Media assets.
- Click the delete icon.
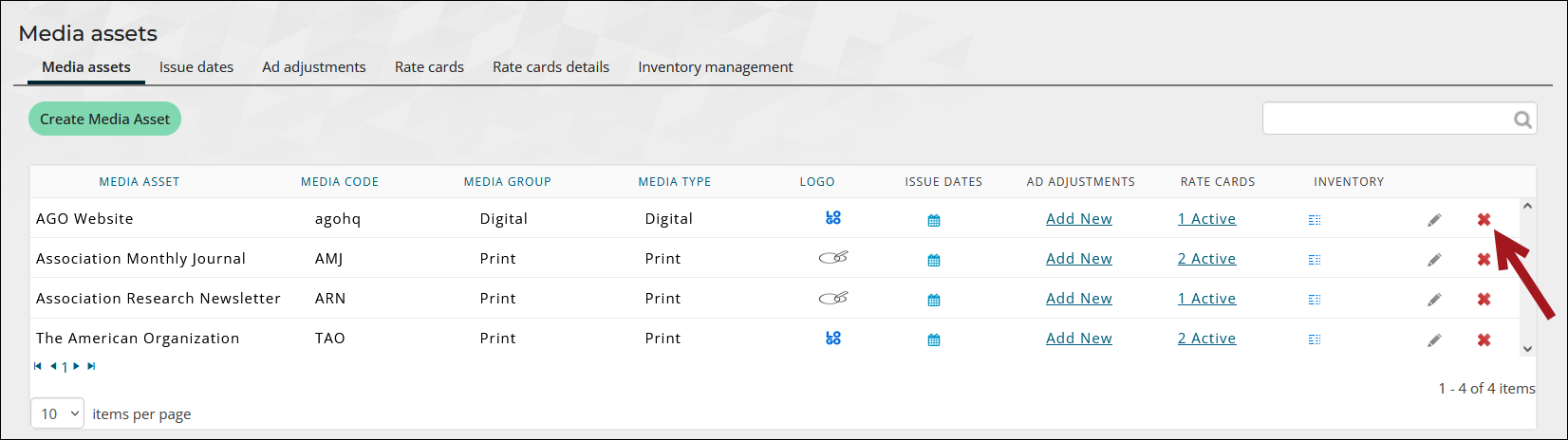
- Click Yes.